Walrus file is a new feature released in Walrus 0.5. It allows you to describe applications and configure infrastructure resources using a concise YAML. You can then execute walrus apply in the Walrus CLI or import it on the Walrus UI. This will submit the Walrus file to the Walrus server, which will deploy, configure, and manage applications and infrastructure resources. This makes it easy to reuse them across multiple environments.
In this tutorial, we will demonstrate how to integrate Walrus CLI with GitLab CI and release applications via Walrus file to improve the CI/CD pipelines.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, please prepare:
Create a new project on GitLab and import our demo project into it. First, ensure that you have the GitHub type
Import Projectpermission enabled. If not, refer to the snapshot below and enable it in theAdmin Area.
Alternatively, you can manually
git clonethe project and push a new GitLab project into it.Install Walrus via
docker run, and expose additional ports30000~30100for NodePort of built-in k3s cluster workload, for more information: https://seal-io.github.io/docs/deploy/standalonesudo docker run -d --privileged --restart=always -p 80:80 -p 443:443 -p 30000-30100:30000-30100 --name walrus sealio/walrus:v0.5.1Access Walrus. In the latest version, Walrus automatically creates a
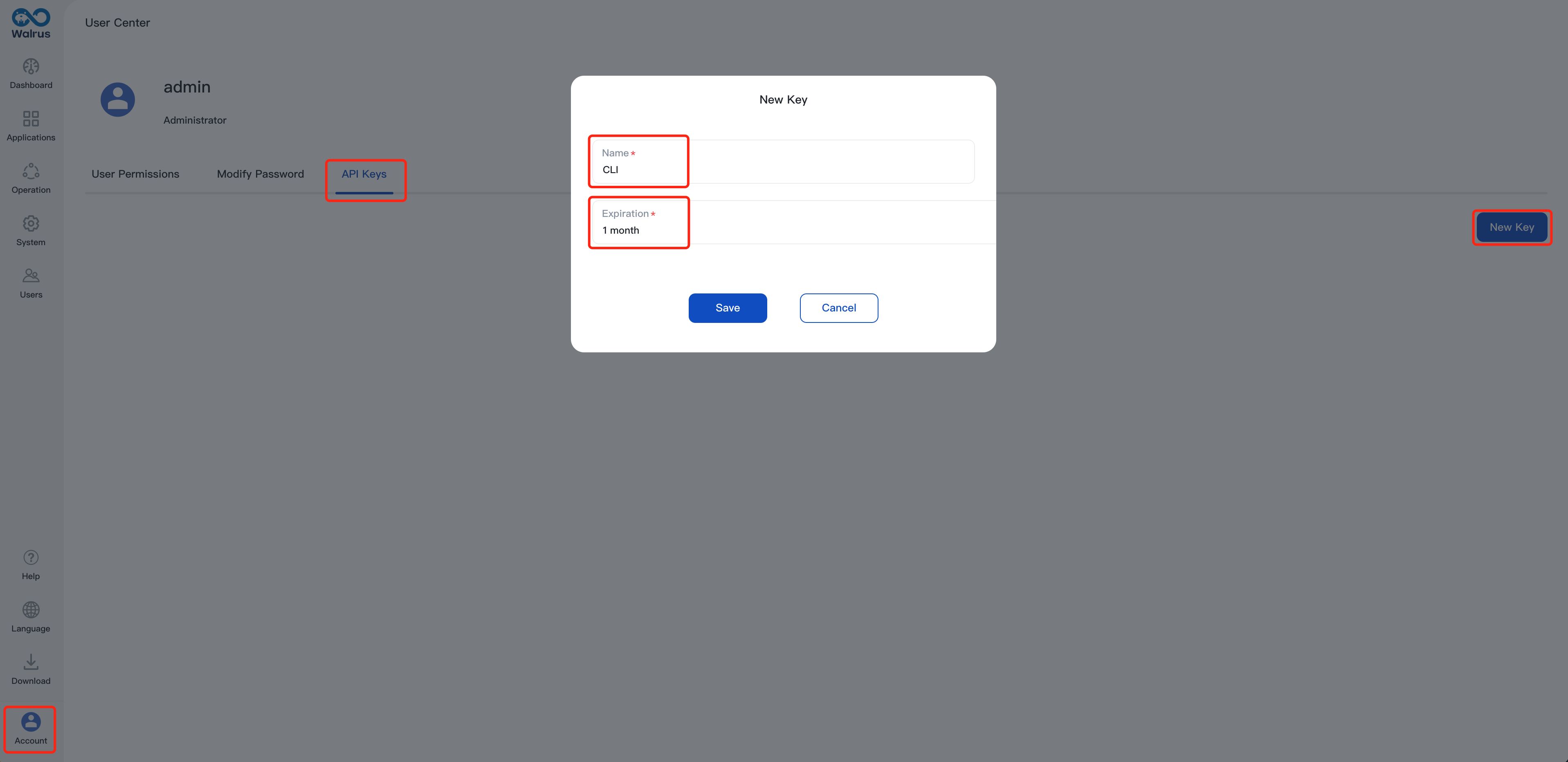
localenvironment in thedefaultproject and adds built-in K3s or other K8s clusters in the Walrus container as a connector in this environment. For demonstration purposes, this example will use the K3s cluster.Create an API key on Walrus to authenticate for communication between the Walrus CLI and Walrus Server in following steps. Here is the guidance:
Navigate to
Account>User center>API KeysClick
New Key, name it and set up expirationAfter configuring, copy the generated key and save it. If the key is lost in the future, it can be regenerated for replacement.
Configure Walrus CLI and Integrate it with GitLab CI
In this section, we will demonstrate an example from CI to CD. Follow the steps below to integrate Walrus CLI with GitLab CI:
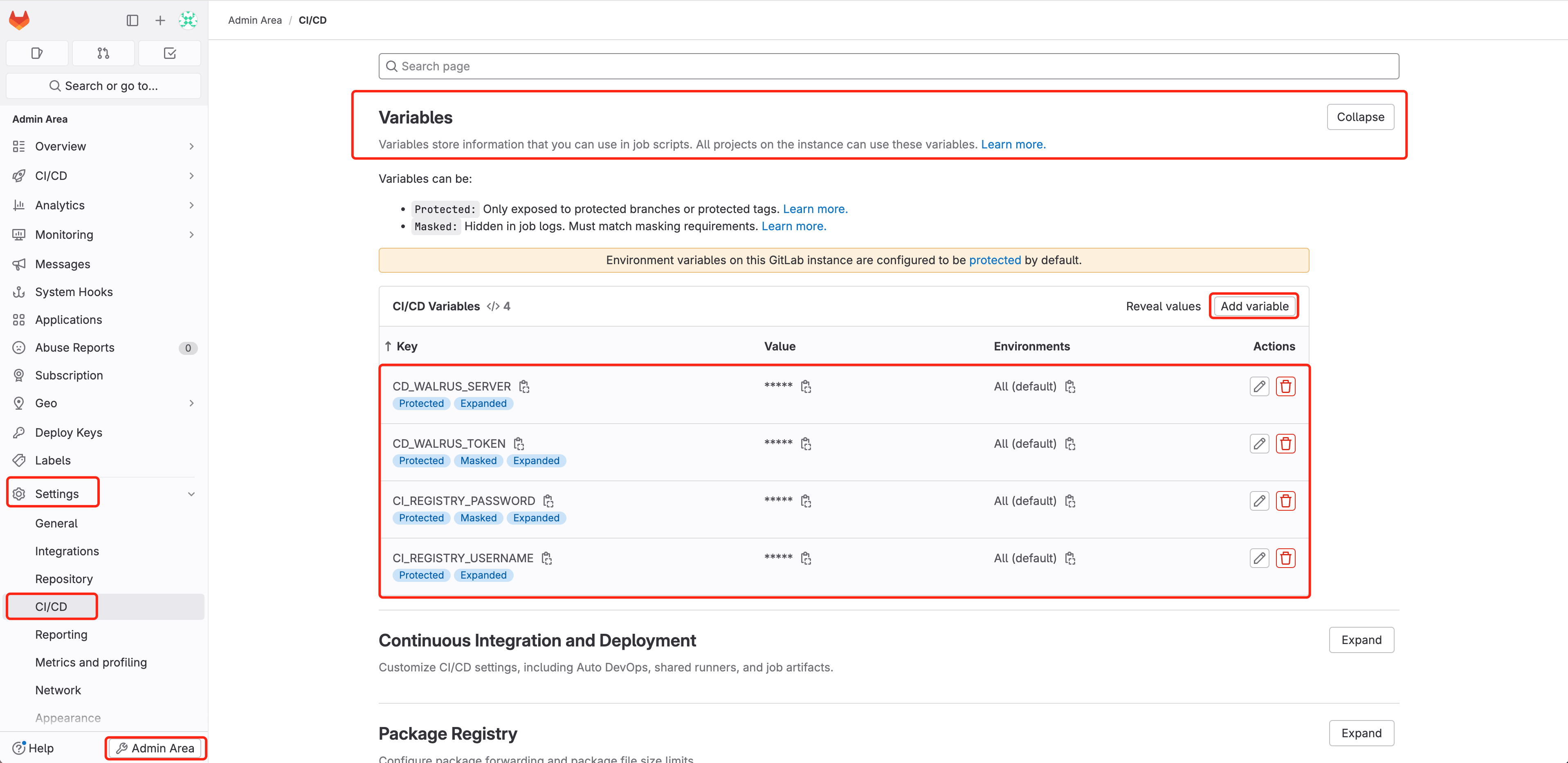
Access GitLab and navigate to
Admin Area > Settings > CI/CD > VariablesAdd following variables, configure the sensitive information that is required by GitLab CI execution:
CI_REGISTRY_USERNAME: The username of the CI build container image to push to Docker Hub, refer to docker login.CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD: The password of the CI build container image to push to Docker Hub, refer to docker login.CD_WALRUS_SERVER: The URL that Walrus accesses, whose format ishttps://domain:port.CD_WALRUS_TOKEN: API Keys of Walrus for authentication.
Create
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile in the GitLab project (exists by default in the sample project), which will define your CI/CD workflow. Below is a sample.gitlab-ci.ymlfile for deploying the sample projectGame 2048. You can copy and modify it as needed, such as changing the imagesealdemo/game2048to your own image name.stages: - compile - build - deploy variables: CI_PROJECT_DIR: ./ CI_IMAGE_NAME: sealdemo/game2048 CD_WALRUS_PROJECT: default CD_WALRUS_PROJECT_ENV: local compile: stage: compile image: maven:3-openjdk-8 artifacts: paths: - target/ script: - mvn clean package build: dependencies: - compile stage: build image: name: gcr.io/kaniko-project/executor:debug entrypoint: [""] artifacts: paths: - target/ before_script: - mkdir -p /kaniko/.docker - echo "{\"auths\":{\"https://index.docker.io/v1/\":{\"auth\":\"$(printf "%s:%s" "${CI_REGISTRY_USERNAME}" "${CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD}" | base64 | tr -d '\n')\"}}}" > /kaniko/.docker/config.json script: - /kaniko/executor --context "${CI_PROJECT_DIR}" --dockerfile "${CI_PROJECT_DIR}/Dockerfile" --destination "${CI_IMAGE_NAME}:${CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA}" deploy: stage: deploy image: alpine before_script: - wget -O walrus --no-check-certificate "${CD_WALRUS_SERVER}/cli?arch=amd64&os=linux" - chmod +x ./walrus script: - ./walrus login --insecure --server ${CD_WALRUS_SERVER} --token ${CD_WALRUS_TOKEN} - ./walrus apply -f ./walrus-file.yaml -p ${CD_WALRUS_PROJECT} -e ${CD_WALRUS_PROJECT_ENV}Check out
walrus-file.yaml, which Walrus uses to deploy applications (already exists by default in the sample project).Walrus fileis a conciseYAMLstructure that describes the application's deployment configuration. You can make any necessary changes to this file:version: v1 resources: - name: game2048 type: containerservice attributes: containers: - profile: run image: ${CI_IMAGE_NAME}:${CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA} ports: - schema: http external: 8080 internal: 8080 protocol: tcp resources: cpu: 0.25 memory: 512Access GitLab, navigate to
Admin Area > CI/CD > Runners, check thatGitLab Runneris online properly(how to install GitLab Runner), which is used to run the CI/CD pipeline defined by.gitlab-ci.yml:
Navigate to
2048 Project > Build > Pipelines, selectRun pipeline
Wait for the pipeline to finish running and check the results of the pipeline run:

View the pipeline's running logs:

The logs indicate that the pipeline ran successfully. GitLab CI completed the CI/CD steps of
Mavenbuild, container image build upload, and application deployment to the K3s cluster using the Walrus CLI, in that specific order.After successfully running the pipelines, you can visit Walrus to view the deployed
game2048application!
Access the 2048 game by using automatically recognized endpoints and the
/2048path. Here is the full URL:http://domain:port/2048.
Now, we have successfully integrated Walrus CLI with GitLab CI. By using the Walrus file in Walrus 0.5.x, developers can now automate the deployment of applications in a more user-friendly way when committing application code to GitLab.
With XaC (Everything is Code), Walrus can unify and manage the entire application lifecycle, from the provisioning infrastructure resources to releasing the upper tier application. This tutorial only covers one scenario. If you are interested in learning more, you can explore other scenarios with Walrus, such as provisioning Kubernetes clusters, creating cloud RDS databases, and configuring LB policies.
If you are interested in Walrus, Welcome to our community:
Discord: https://discord.gg/fXZUKK2baF
Twitter/X: https://twitter.com/Seal_io
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/seal-io
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@Seal-io
